Education Inequality: A Barrier to Social Progress
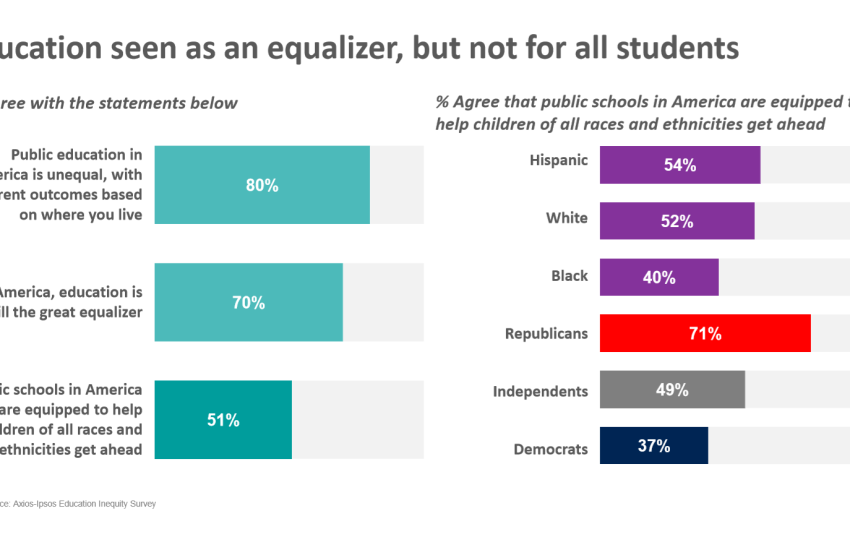
Education is often referred to as the great equalizer, providing individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to succeed in life. However, when it comes to education inequality, this premise is far from reality. Education inequality refers to the disparity in access to quality education and resources for individuals based on various factors such as socioeconomic status, race, and geographic location. This disparity not only affects individuals but also hinders social progress as a whole.
Access to Quality Education
One of the most significant impacts of education inequality is the lack of access to quality education for marginalized communities. Low-income neighborhoods often have underfunded schools, outdated resources, and inexperienced teachers, leading to a subpar education for students. This lack of quality education perpetuates a cycle of poverty and limits opportunities for social mobility.
Socioeconomic Disparities
Education is often seen as a pathway to economic success. However, education inequality exacerbates socioeconomic disparities, creating a divide between the wealthy and the disadvantaged. Students from affluent families have access to private schools, tutors, and extracurricular activities that enhance their educational experience. On the other hand, students from low-income families struggle to afford basic necessities, let alone quality education resources.
Racial and Ethnic Disparities
Education inequality also manifests in racial and ethnic disparities. Minority students are disproportionately affected by inadequate resources, discrimination, and bias within the education system. This leads to lower graduation rates, limited opportunities for higher education, and systemic barriers to success. As a result, these students are more likely to face poverty, unemployment, and other social challenges.
The Cycle of Inequality
Education inequality perpetuates a vicious cycle of poverty, unemployment, and social stratification. When individuals do not have access to quality education, they are less likely to secure stable employment, achieve economic stability, or contribute positively to society. This cycle of inequality not only affects individuals but also weakens the social fabric as a whole.
Breaking the Cycle
Addressing education inequality is crucial for social progress. By investing in resources and support for marginalized communities, we can level the playing field and provide equal opportunities for all individuals. This includes increasing funding for underprivileged schools, implementing equitable policies, and promoting diversity and inclusion within the education system.
Empowering Communities
Empowering communities to advocate for quality education is essential in combating education inequality. By engaging parents, educators, policymakers, and other stakeholders, we can work together to create a more equitable and inclusive education system. This collaborative effort can lead to positive changes in the way education is accessed and delivered to all individuals.
Conclusion
Education inequality is a significant barrier to social progress. It limits opportunities for individuals, perpetuates socioeconomic disparities, and hinders overall development. By addressing education inequality and empowering communities to advocate for change, we can work towards a more equitable and inclusive society where all individuals have access to quality education and opportunities for success. As we strive for social progress, let us not forget that education is the key to unlocking a brighter future for all.