How Parenting Styles Affect Child Development
Parenting styles play a crucial role in shaping the development of a child. The way parents interact with their children, set rules, and provide support can have lasting effects on their cognitive, emotional, and social development.
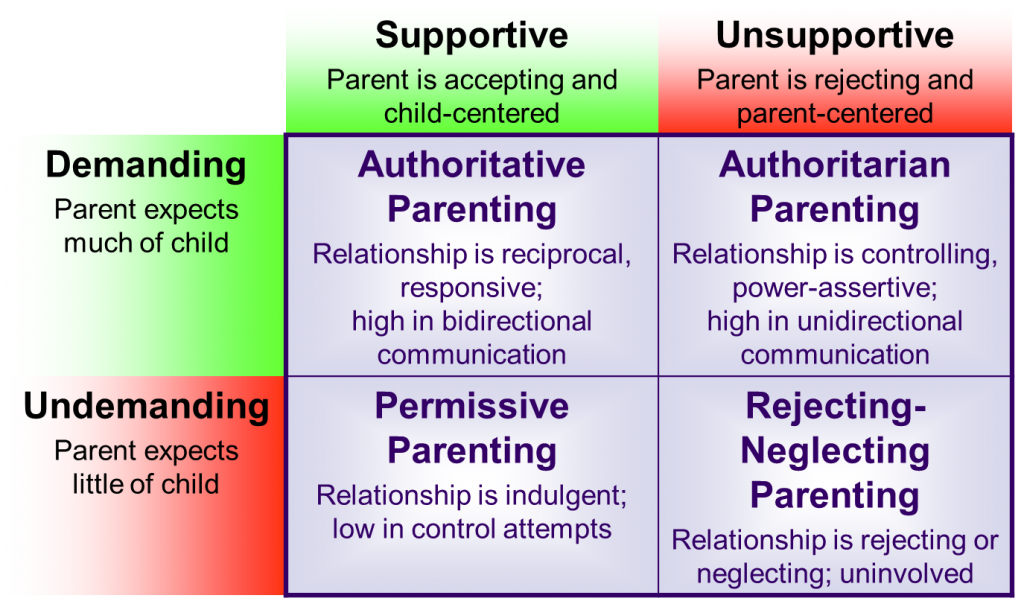
Authoritative Parenting
Authoritative parenting is often considered the most effective parenting style. This approach involves setting clear rules and boundaries while also being responsive and warm towards the child. Parents who practice authoritative parenting are empathetic and understanding, but also firm in enforcing rules.
Research has shown that children raised by authoritative parents tend to have higher self-esteem, better social skills, and are more academically successful. These children also have lower rates of behavior problems and are more resilient in the face of challenges.
Authoritarian Parenting
Authoritarian parenting is characterized by strict rules and high expectations, but with little warmth or responsiveness towards the child. Parents who adopt this style often use punishment as a means of control and prioritize obedience above all else.
Children raised by authoritarian parents may struggle with self-esteem, have difficulty forming meaningful relationships, and exhibit higher levels of anxiety and depression. They may also have trouble developing independence and self-regulation skills.
Permissive Parenting
Permissive parenting involves being warm and responsive towards the child but setting few rules or boundaries. Parents who practice permissive parenting may avoid confrontation and prioritize their child’s happiness over discipline.
Children raised by permissive parents may struggle with self-control, have poor academic performance, and exhibit behavior problems. They may also have trouble coping with frustration and may lack a sense of personal responsibility.
Uninvolved Parenting
Uninvolved parenting is characterized by low levels of warmth, responsiveness, and control. Parents who are uninvolved may be neglectful or emotionally distant, providing little to no support or guidance to their children.
Children raised by uninvolved parents are at increased risk for a range of negative outcomes, including poor academic performance, low self-esteem, and behavioral issues. They may also experience difficulties forming healthy relationships and have a higher likelihood of engaging in risky behaviors.
Conclusion
Parenting styles have a profound impact on child development. By understanding the differences between authoritative, authoritarian, permissive, and uninvolved parenting, parents can make informed decisions about how to best support their child’s growth and well-being. Through a balance of warmth, responsiveness, and appropriate discipline, parents can help their children thrive and reach their full potential.